Basics about Escalation points
If you want to escalate from Organisation area A to Organisation area B, there has to be an escalation point that allows escalation, for example named Escalation point A to B.
When you want to allow a contact to escalate from one organisation area to another during routing in ACE Admin, you choose an escalation point which transfers the contact to another organisation area instead of a queue/waiting list. For further information on how to administrate escalation points see instructions for ACE Admin.
Via the reports in ACE Report you can subsequently follow the flow of contacts between the organisation areas.
A contact can
- arrive via an escalation point to an organisation area,
- be escalated via an escalation point from an organisation area.
This applies to all services, i.e. incoming IVR calls, outgoing callback and incoming emails and chats. Note that campaign calls cannot be escalated. By separately presenting the inward and outward flow from an organisation area via escalation points, you do not mix up the flow of ‘”physical” contacts (e.g. physical calls) with escalations between organisation areas.
The following scenario shows the principle for the incoming IVR call service.
A call comes in via IVR to organisation area A. The call is escalated to organisation area B. The call is answered by an agent in organisation area B.
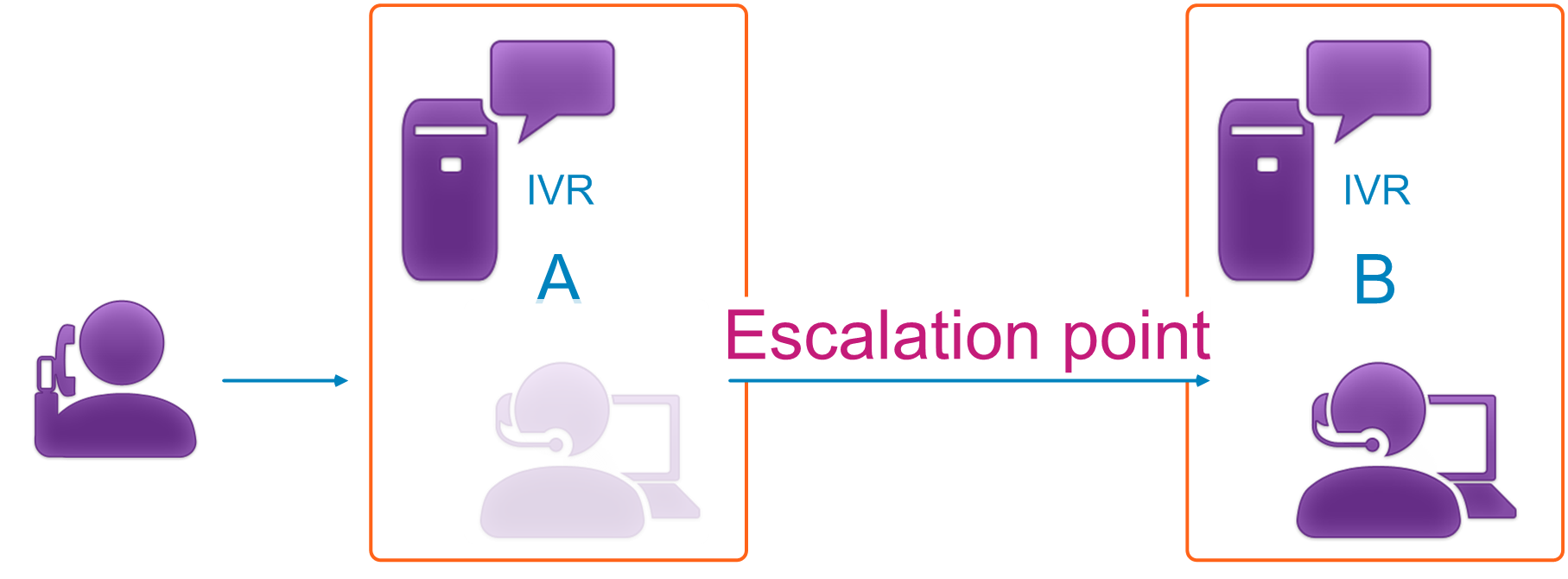
The scenario gives the following basic presentation in the task statistics:
| Organisation area | Customer service requested | Received from another organisation area | Escalated to another organisation area | Answered call |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| B | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
Note that for a particular organisation area you cannot identify to/from which organisation areas the escalation has taken place.