For each system using ACE Chat, there must be at least one ACE Chat Engine installed exclusively for the system. ACE Chat Engine is exposed to the Internet and acts as a protective layer between the chatting customers on the Internet and the ACE Server. See Configuration Instructions ACE Chat for details.
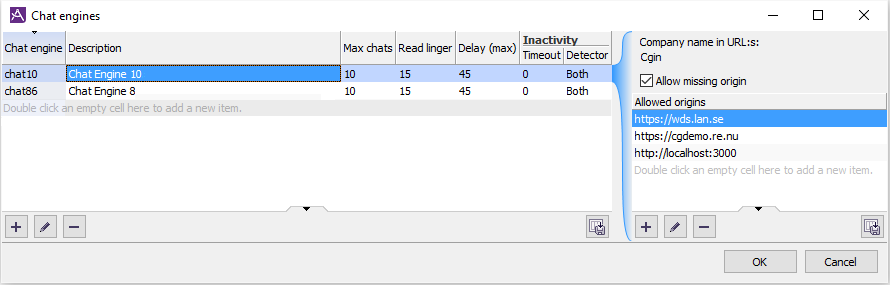
In the Chat engines window you configure parameters for the chat engines installed for the system. The chat engines are shared by all organisation areas in your ACE solution.
See Chat configuration made in ACE Admin for requirements on access rights.

origin header. Some web browsers omit this when sending a request to the same domain as the web page. The header might also be configured to be omitted in Internet Explorer.The URL-adapted company name is shown in this window since the configuration of allowed origins made in this window is also required in the company's web pages using ACE Web SDK to start a chat. The URL-adapted company name must be included in the URL loading ACE Web SDK. See Configuration Instructions ACE Web SDK for details.
If the configuration of company name for URL:s is missing, the configuration of allowed origins in this window will not be used by ACE Web SDK and this will be indicated in the window. Configuration of company name for URL:s is made in the System parameters for interfaces window .
Here are two scenarios where more than one chat engine is used by the same ACE system.
Agents cannot use ACE Agent or ACE Interact to chat directly with each other. However, if you want to use chat internally, you could use ACE Chat. Anyone who wants to initiate a chat session with a colleague uses a designated page on the Intranet to request internal chat. Thus, agents are able to receive chat requests in ACE Agent or ACE Interact from their co-workers in the same way as for external customers.
In this scenario, the company thus offers chat on the company's public web pages as well as on internal web pages. The internal chat should not be possible to access from the public web pages and vice versa. In order to solve this problem, two instances of ACE Chat Engine could be installed and configured in ACE Admin. One connected to the Internet and one only connected to the company's internal network. The configuration of allowed origins would differ and public chat entrances would be connected to the public chat engine together with internal entrances connected to the internal chat engine. Even if both ACE Chat Engines would be connected to the Internet, it would be impossible to start a chat on one of the internal chat entrances from public web pages provided that the configuration of allowed origins prevents this.
To achieve redundancy in the system, two instances of ACE Chat Engine could be installed on different server computers. The configured name of the chat engines would be the same (i.e. only one chat engine would be configured in ACE Admin). By doing so, the same configuration would be reflected to both instances of ACE Chat Engine. To make the redundant solution complete, a proxy or load balancer would have to be added to direct chat sessions to either of the two instances in a random or round-robin manner (but all messages for the same session must be directed to the same instance).